 Home
Home
 Back
Back
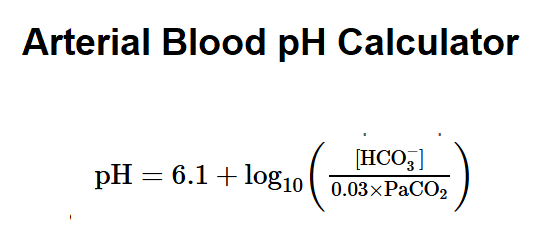
The Arterial Blood pH Calculator estimates the acidity (pH) of arterial blood using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, which is based on bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻) and arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure (PaCO₂). The formula used is:
Where:
Enter the bicarbonate and PaCO₂ values to compute the arterial blood pH.
This calculator is designed to assist healthcare professionals in assessing acid-base balance and diagnosing conditions such as acidosis or alkalosis by estimating arterial blood pH.
Input the bicarbonate concentration (in mEq/L) and PaCO₂ (in mmHg). The calculator will display the arterial blood pH value and indicate whether it suggests acidosis, alkalosis, or normal pH.
Normal pH Ranges:
Example: Calculate the pH for bicarbonate = 24 mEq/L and PaCO₂ = 40 mmHg.
Use this tool for quick and accurate pH calculations in clinical settings, but consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment decisions.